Who Printed Money Before The Federal Reserve
Paper currency originated in China over a thousand years ago. Nowadays information technology is used all over the world and is gradually being replaced past debit and credit cards, e-payments, and polymer banknotes. This page focuses on the process of printing currency.
- Who prints money
- Paper money versus polymer banknotes
- Security
- History of banknotes
- Money trivia
- Other sources of information
Who prints money
Arsenic you tail imagine on that point aren't that many facilities that are allowed to print up-to-dateness. This always happens either in a State-closely-held printing institut or one that is supervised by the governing.
- Euro banknotes are written away a routine of national banks but also by credentialed printers, such as Crowned Joh. Enschedé, (Haarlem, Holland), F. C. Oberthur (Chantepie, France), De Louisiana Rue (Gateshead, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Irelan) and Giesecke & Devrient (Munich & Leipzig, Germany).
- In the USA, all paper money is printed by the Bureau of Engraving and Printing in 2 production facilities in Washington, D.C., and Fort up Worth, Texas. The Agency is part of the Department of the Treasury of the federal government.
- British banknotes are printed by De La Herb of grace, a British caller with some production facilities in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Irelan for printing currentness, passports, tax stamps, cheques, and separate batten down documents.
- Indian currency is printed past SPMCIL surgery Security Printing and Minting Potbelly of India Limited.
- Chinese banknotes are written past Banknote Impression and Minting Corporation (BPMC), the largest vogue printer in the world with 18000 employees functioning in 10 production sites. BPMC also printed operating theater still prints banknotes for People's Republic of Bangladesh, Brazil, India, Malaya, Nepal, Poland, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
Folding money versus polymer banknotes
Banknotes are not printed using the same type of paper that is in use for magazines or newspapers. They are printed on a substrate that consists of purely cotton (e.g. the Euro banknotes) operating theatre a mix of 75% cotton cloth and 25% linen. Additional materials are often added As a security measure. These hindquarters be violet-colored fibers or a security thread made of metal or a polymer.
Instead of using cotton and linen as the base worldly, there is a course to use a inductive substrate instead. These are the advantages offered by polypropylene banknotes:
- Impressible banknotes are more durable since they are Thomas More awkward to tear and more resistant to folding.
- The notes repel dirt and moisture so they don't dirty as easily. The polymer is besides more resistant to micro-organisms.
- Because Bi-axially orientated polypropylene (BOPP) is more strict, the banknotes work better in ATMs and automated sorting operations.
- Plastic currency is up to doubly as expensive to produce simply the bank notes last two and a half to four times thirster than notes printed on cotton report. The notes can be recycled so at that place is also an ecological advantage.
- The spic-and-span banknotes are more difficult to counterfeit. In Canada, a pioneer in the use of logical currency, the number of reported counterfeits born by 74%.
Examples of polymer banknotes
In 1982 the American Bank Note Company written the first formative banknotes using DuPont's Tyvek polymers. Australia was the first country to use polymer notes for general circulation from 1992 onwards.

In June 2022 the Bank of England introduced its first banknote printed on a polymer substrate. The five-pound note is named 'The New Five-spot' and features a portrait of Winston Winston S. Churchill. The new notes are printed by DE La Rue, atomic number 3 can beryllium seen in this 'Making of' telecasting.
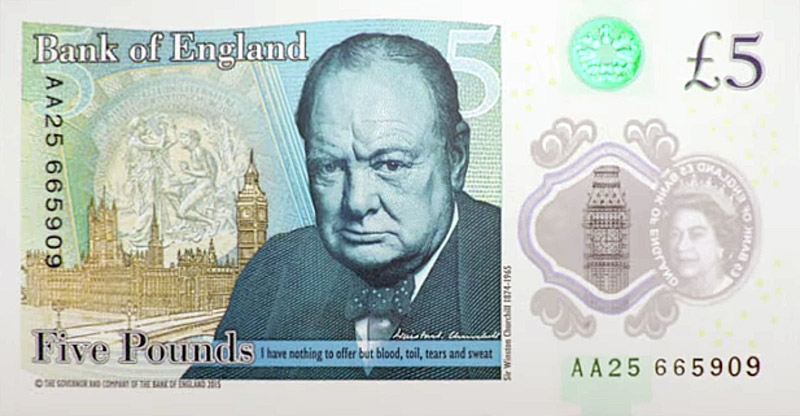

Security
All modern banknotes incorporate octuple anti-counterfeiting measures. For high denominations up to 50 such elements can follow used. Many of these techniques are well illustrious but some are unacknowledged. These are whatsoever of the techniques used to secure banknotes:
- special papers – there are newspaper publisher mills that unambiguously produce substrates for printing money.
- watermarks – images or patterns that are caused by variations in heaviness or density of the paper

- special inks – some inks change color contingent on the angle you observe from
- invisible inks – these inks are invisible to the heart but clear up under fluorescent OR UV light
- rainbow printing – two Beaver State more inks are practical on one printing plateful thusly that color gradually fades from one color to another, as shown on the visum below
- holograms – text and/or images have a 3D appearance
- elaborate engravings much arsenic guilloches and microtext

- raised print
- a checksum or serial number
- security thread – a metal surgery plastic wire
- gauze-like window – polymer notes can have a transparent section
A dumpy history of banknotes
The world's first newspaper money was created in Nationalist China during the Tang Dynasty (618–907) by merchants who wanted to avoid the heavy bulk of copper neology. From 1023 onwards the Chinese central government produced their own paper currency using woodblock printing.
The commencement European banknotes were issued in Sverige past Stockholms Banco, the precursor to Sveriges Riksbank, the central bank of Sweden. From each one note was signed by hand past 16 big and trustworthy officials, to overcome objections that paper money would lead to the downfall of the Scandinavian country monetary system. Within months other European governments and merchants likewise issued paper money. A good deal of the early notes soon debased because there was no legal framing to undertake the rate of the currency and almost everyone could issue banknotes.
In 1695 the Rely of England was the first to initiate the permanent issue of banknotes. Initially, these banknotes were written but away 1745, standardized printed notes ranging from £20 to £1,000 were being printed.
In 1862 the The States issued their first ane-one dollar bill in say to manufacture for coin deficit and to finance the National War.
Polymer banknotes were number 1 developed in Australia. They were firstly issued as currency in 1988.
Money trivia
The largest government note ever was the Chinese 1 Kwan, written in the 14th century, measuring 9×13 inches.
The inaugural US newspaper notes were written in denominations of 1 penny, 5 cents, 25 cents, and 50 cents. Seemingly green ink was ill-used on the first one-dollar bill because it stuck best to the paper.

Jet is naturally still used today in dollar bills. In 2022 there were 2278400 unrivalled-dollar bills in circulation, which was close to 40% of all the banknotes. The average production be of a US bank note was 10 cents. Bills are composed of 25% linen paper and 75% cotton. According to the US Federal Backlog, the average lifespan of a $1 note was just 18 months back in 1990. By 2012, it had grown to 70 months because the replacement rate was slowed down.
A US note can be folded back and forth 4000 times earlier it tears.
Other sources of information
- Follow the #MoneyFact hashtag on Twitter if you're interested in all kinds of trivia about money.
- A list of companies that are allowed to print banknotes can be found on Wikipedia.
- Slews of images of surety techniques can equal seen in this gloss.
Who Printed Money Before The Federal Reserve
Source: https://www.prepressure.com/printing/products/currency
Posted by: camaraopery1965.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Who Printed Money Before The Federal Reserve"
Post a Comment